Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
TikTok wants users to believe that errors blocking uploads of anti-ICE videos or direct messages mentioning Jeffrey Epstein are due to technical errors—not the platform seemingly shifting to censor content critical of Donald Trump after he hand-picked the US owners who took over the app last week.
However, experts say that TikTok users' censorship fears are justified, whether the bugs are to blame or not.
Ioana Literat, an associate professor of technology, media, and learning at Teachers College, Columbia University, has studied TikTok's politics since the app first shot to popularity in the US in 2018. She told Ars that "users' fears are absolutely justified" and explained why the "bugs" explanation is "insufficient."
"Even if these are technical glitches, the pattern of what's being suppressed reveals something significant," Literat told Ars. "When your 'bug' consistently affects anti-Trump content, Epstein references, and anti-ICE videos, you're looking at either spectacular coincidence or systems that have been designed—whether intentionally or through embedded biases—to flag and suppress specific political content."
TikTok users are savvy, Literat noted, and what's being cast as "paranoia" about the app's bugs actually stems from their "digital literacy," she suggested.
"They've watched Instagram suppress Palestine content, they've seen Twitter's transformation under Musk, they've experienced shadow-banning and algorithmic suppression, including on TikTok prior to this," Literat said. "So, their pattern recognition isn't paranoia, but rather digital literacy."
Casey Fiesler, an associate professor of technology ethics and internet law at the University of Colorado, Boulder, agreed that TikTok's "bugs" explanation wasn't enough to address users' fears. She told CNN that TikTok risks losing users' trust the longer that errors damage the perception of the app.
"Even if this isn’t purposeful censorship, does it matter? In terms of perception and trust, maybe," Fiesler told CNN.
Some users are already choosing to leave TikTok. A quick glance at the TikTok subreddit shows many users grieving while vowing to delete the app, Literat pointed out, though some are reportedly struggling to delete accounts due to technical issues. Even with some users blocked from abandoning their accounts, however, "the daily average of TikTok uninstalls are up nearly 150 percent in the last five days compared to the last three months," data analysis firm Sensor Tower told CNN.
A TikTok USDS spokesperson told Ars that US owners have not yet made any changes to the algorithm or content moderation policies. So far, the only changes have been to the US app's terms of use and privacy policy, which impacted what location data is collected, how ads are targeted, and how AI interactions are monitored.
For TikTok, the top priority appears to be fixing the bugs, which were attributed to a power outage at a US data center. A TikTok USDS spokesperson told NPR that TikTok is also investigating the issue where some users can't talk about Epstein in DMs.
"We don't have rules against sharing the name 'Epstein' in direct messages and are investigating why some users are experiencing issues," TikTok's spokesperson said.
TikTok's response came after California governor Gavin Newsom declared on X that "it’s time to investigate" TikTok.
"I am launching a review into whether TikTok is violating state law by censoring Trump-critical content," Newsom said. His post quote-tweeted an X user who shared a screenshot of the error message TikTok displayed when some users referenced Epstein and joked, "so the agreement for TikTok to sell its US business to GOP-backed investors was finalized a few days ago," and "now you can’t mention Epstein lmao."
As of Tuesday afternoon, the results of TikTok's investigation into the "Epstein" issue were not publicly available, but TikTok may post an update here as technical issues are resolved.
"We've made significant progress in recovering our US infrastructure with our US data center partner," TikTok USDS's latest statement said. "However, the US user experience may still have some technical issues, including when posting new content. We're committed to bringing TikTok back to its full capacity as soon as possible. We'll continue to provide updates."
TikTokers will notice subtle changes, expert says
For TikTok's new owners, the tech issues risk confirming fears that Trump wasn't joking when he said he'd like to see TikTok be tweaked to be "100 percent MAGA."
Because of this bumpy transition, it seems likely that TikTok will continue to be heavily scrutinized once the USDS joint venture officially starts retraining the app on US data. As the algorithm undergoes tweaks, frequent TikTok users will likely be the first to pick up on subtle changes, especially if content unaligned with their political views suddenly starts appearing in their feeds when it never did before, Literat suggested.
Literat has researched both left- and right-leaning TikTok content. She told Ars that although left-leaning young users have for years loudly used the app to promote progressive views on topics like racial justice, gun reforms, or climate change, TikTok has never leaned one way or the other on the political spectrum.
Consider Christian or tradwife TikTok, Literat suggested, which grew huge platforms on TikTok alongside leftist bubbles advocating for LGBTQ+ rights or Palestine solidarity.
"Political life on TikTok is organized into overlapping sub-communities, each with its own norms, humor, and tolerance for disagreement," Literat said, adding that "the algorithm creates bubbles, so people experience very different TikToks."
Literat told Ars that she wasn't surprised when Trump suggested that TikTok would be better if it were more right-wing. But what concerned her most was the implication that Trump viewed TikTok "as a potential propaganda apparatus" and "a tool for political capture rather than a space for authentic expression and connection."
"The historical irony is thick: we went from 'TikTok is dangerous because it's controlled by the Chinese government and might manipulate American users' to 'TikTok should be controlled by American interests and explicitly aligned with a particular political agenda,'" Literat said. "The concern was never really about foreign influence or manipulation per se—it was about who gets to do the influencing."
David Greene, senior counsel for the Electronic Frontier Foundation, which fought the TikTok ban law, told Ars that users are justified in feeling concerned. However, technical errors or content moderation mistakes are nearly always the most likely explanations for issues, and there's no way to know "what's actually happening." He noted that lawmakers have shaped how some TikTok users view the app after insisting that they accept that China was influencing the algorithm without providing evidence.
"For years, TikTok users were being told that they just needed to follow these assumptions the government was making about the dangers of TikTok," Greene said. And "now they're doing the same thing, making these assumptions that it's now maybe some content policy is being done either to please the Trump administration or being controlled by it. We conditioned TikTok users to basically to not have trust in the way decisions were made with the app."
MAGA tweaks risks TikTok's "death by a thousand cuts"
TikTok USDS likely wants to distance itself from Trump's comments about making the app more MAGA. But new owners have deep ties with Trump, including Larry Ellison, the chief technology officer of Oracle, whom some critics suggest has benefited more than anyone else from Trump's presidency. Greene noted that Trump's son-in-law, Jared Kushner, is a key investor in Silver Lake. Both firms now have a 15 percent stake in the TikTok USDS joint venture, as well as MGX, which also seems to have Trump ties. CNBC reported MGX used the Trump family cryptocurrency, World Liberty Financial, to invest $2 billion in Binance shortly before Trump pardoned Binance's CEO from money laundering charges, which some viewed as a possible quid pro quo.
Greene said that EFF warned during the Supreme Court fight over the TikTok divest-or-ban law that "all you were doing was substituting concerns for Chinese propaganda, for concerns for US propaganda. That it was highly likely that if you force a sale and the sale is up to the approval of the president, it's going to be sold to President's lackeys."
"I don't see how it'd be good for users or for democracy, for TikTok to have an editorial policy that would make Trump happy," Greene said.
If suddenly, the app were tweaked to push more MAGA content into more feeds, young users who are critical of Trump wouldn't all be brainwashed, Literat said. They would adapt, perhaps eventually finding other apps for activism.
However, TikTok may be hard to leave behind at a time when other popular apps seem to carry their own threats of political suppression, she suggested. Beyond the video-editing features that made TikTok a behemoth of social media, perhaps the biggest sticking point keeping users glued to TikTok is "fundamentally social," Literat said.
"TikTok is where their communities are, where they've built audiences, where the conversations they care about are happening," Literat said.
Rather than a mass exodus, Literat expects that TikTok's fate could be "gradual erosion" or "death by a thousand cuts," as users "likely develop workarounds, shift to other platforms for political content while keeping TikTok for entertainment, or create coded languages and aesthetic strategies to evade detection."
CNN reported that one TikTok user already found that she could finally post an anti-ICE video after claiming to be a "fashion influencer" and speaking in code throughout the video, which criticized ICE for detaining a 5-year-old named Liam Conejo Ramos.
"Fashion influencing is in my blood," she said in the video, which featured "a photo of Liam behind her," CNN reported. "And even a company with bad customer service won’t keep me from doing my fashion review."
Short-term, Literat thinks that longtime TikTok users experiencing inconsistent moderation will continue testing boundaries, documenting issues, and critiquing the app. That discussion will perhaps chill more speech on the platform, possibly even affecting the overall content mix appearing in feeds.
Long-term, however, TikTok's changes under US owners "could fundamentally reshape TikTok's role in political discourse."
"I wouldn’t be surprised, unfortunately, if it suffers the fate of Twitter/X," Literat said.
Literat told Ars that her TikTok research was initially sparked by a desire to monitor the "kind of authentic political expression the platform once enabled." She worries that because user trust is now "damaged," TikTok will never be the same.
"The tragedy is that TikTok genuinely was a space where young people—especially those from marginalized communities—could shape political conversations in ways that felt authentic and powerful," Literat said. "I’m sad to say, I think that's been irretrievably broken."

The chair of a federal vaccine advisory panel under anti-vaccine Health Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr. made his stance clear on vaccines in a podcast last week—and that stance was so alarming that the American Medical Association was compelled to respond with a scathing statement.
Kirk Milhoan, who was named chair of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices for the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in December, appeared on the aptly named podcast "Why Should I Trust You." In the hour-long interview, Milhoan made a wide range of comments that have concerned medical experts and raised eyebrows.
Early into the discussion, Milhoan, a pediatric cardiologist, declared, "I don't like established science," and that "science is what I observe." He lambasted the evidence-based methodology that previous ACIP panels used to carefully and transparently craft vaccine policy.
While arguing that he was not anti-vaccine, he said he was merely focused on safety and made false claims about vaccine risks, a common trope among anti-vaccine activists. He falsely linked vaccines to allergies, asthma, and eczema and repeated a claim, without evidence, that COVID-19 vaccines killed children. When pressed by the podcast hosts, he revealed that he put the risk of vaccine side effects on the same footing as the risks from the diseases the shots prevent—despite the fact that disease risks are often orders of magnitude larger than the tiny risks from vaccines.
In response to pushback from the hosts, Milhoan objected to the idea that the measles and polio vaccines reduced the spread of those diseases. He went further, questioning the need for those vaccines as well as routine vaccinations, generally.
"I think also as you look at polio, we need to not be afraid to consider that we are in a different time now than we were then," he said, referring to the time before the first polio vaccines were developed in the 1950s. "Our sanitation is different. Our risk of disease is different. And so those all play into the evaluation of whether this is worthwhile of taking a risk for a vaccine or not."
He then pondered out loud what would happen if people stopped getting vaccinated. "If we take away all of the herd immunity, then does that switch, does that teeter-totter switch in a different direction?" he asked.
Backlash
In a statement, AMA Trustee Sandra Adamson Fryhofer blasted the question. "This is not a theoretical debate—it is a dangerous step backward," she said. "Vaccines have saved millions of lives and virtually eliminated devastating diseases like polio in the United States. There is no cure for polio. When vaccination rates fall, paralysis, lifelong disability, and death return. The science on this is settled."
Fryhofer also took aim at Milhoan's repeated argument that the focus of vaccination policy should move from population-level health to individual autonomy. Moving away from routine immunizations, which include discussions between clinicians and patients, "does not increase freedom—it increases suffering," she said, adding that the weakening of recommendations "will cost lives."
Overall, Milhoan's comments only further erode the relevance of ACIP and federal vaccine policy among the medical community and states. According to a KFF policy brief, 27 states and Washington, DC, have already announced they will not follow current CDC vaccine recommendations, which Kennedy dramatically overhauled earlier this month without even consulting the ACIP. Instead, the majority of states are relying on previous recommendations or recommendations made within states or by medical organizations.
On Monday, the American Academy of Pediatrics announced the 2026 update to its childhood and adolescent vaccine schedule, which it has held up as an alternative to the CDC's schedule and has been widely embraced by pediatricians. In the announcement, AAP noted that 12 other medical organizations have endorsed the schedule, including the AMA, the American Academy of Family Physicians, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the Infectious Diseases Society of America, and the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society.
The AAP's updated recommendations are largely the same as the schedule from last year, but it is significantly different from the CDC's recommendations, which "depart from longstanding medical evidence and no longer offer the optimal way to prevent illnesses in children," the AAP said.
“The AAP will continue to provide recommendations for immunizations that are rooted in science and are in the best interest of the health of infants, children and adolescents of this country,” AAP President Andrew Racine said in the announcement.

The US Department of Transportation apparently thinks it's a good idea to use artificial intelligence to draft rules impacting the safety of airplanes, cars, and pipelines, a ProPublica investigation revealed Monday.
It could be a problem if DOT becomes the first agency to use AI to draft rules, ProPublica pointed out, since AI is known to confidently get things wrong and hallucinate fabricated information. Staffers fear that any failure to catch AI errors could result in flawed laws, leading to lawsuits, injuries, or even deaths in the transportation system.
But the DOT's top lawyer, Gregory Zerzan, isn't worried about that, December meeting notes revealed, because the point isn't for AI to be perfect. It's for AI to help speed up the rulemaking process, so that rules that take weeks or months to draft can instead be written within 30 days. According to Zerzan, DOT's preferred tool, Google Gemini, can draft rules in under 30 minutes.
"We don’t need the perfect rule on XYZ," Zerzan told DOT staffers at the meeting. "We don’t even need a very good rule on XYZ. We want good enough."
DOT staffers "deeply skeptical" of Gemini
ProPublica spoke to experts and granted six DOT staffers anonymity to discuss their concerns about DOT's use of Google Gemini to draft rules.
Some experts who monitor AI use in government told ProPublica that DOT could save time using Gemini as a research assistant "with plenty of supervision and transparency." For example, at a presentation, DOT staffers were told that "most of what goes into the preambles of DOT regulatory documents is just 'word salad,'" and "Gemini can do word salad."
However, staffers told ProPublica they felt "deeply skeptical" that Gemini was up to the task. They emphasized that DOT rulemaking is "intricate work" requiring sometimes decades of "expertise in the subject at hand as well as in existing statutes, regulations, and case law." Likely unsettling staffers further, ProPublica noted that a demonstration of Gemini's rule-drafting produced a document missing key text, which a staffer would then have to fill in. Additionally, the DOT's move comes after a year of AI hallucinations scrambling courts, with many lawyers fined and even judges admitting they can be fooled by fabricated information.
Any errors in the rules could have serious consequences. These rules "touch virtually every facet of transportation safety," keeping "airplanes in the sky," preventing "gas pipelines from exploding," and stopping "freight trains carrying toxic chemicals from skidding off the rails," ProPublica reported.
“It seems wildly irresponsible,” one staffer said.
Despite staffers' concerns, DOT appears to be racing forward with the plan, ProPublica reported. The department has already used Gemini to draft a "still-unpublished Federal Aviation Administration rule, according to a DOT staffer briefed on the matter."
Trump "very excited" about AI drafting rules
Donald Trump has urged federal agencies to adopt AI at a rapid pace, but nowhere in his orders has the president pushed for AI to draft laws, ProPublica noted.
However, Trump is “very excited" about the DOT initiative, Zerzan told staffers at the meeting, suggesting that Trump sees DOT as the "point of the spear" and expects other agencies to follow its lead.
At DOT, Trump likely hopes to see many rules quickly updated to modernize airways and roadways. In a report highlighting the Office of Science and Technology Policy's biggest "wins" in 2025, the White House credited DOT with "replacing decades-old rules with flexible, innovation-friendly frameworks," including fast-tracking rules to allow for more automated vehicles on the roads.
Right now, DOT expects that Gemini can be relied on to "handle 80 to 90 percent of the work of writing regulations," ProPublica reported. Eventually all federal workers who rely on AI tools like Gemini to draft rules "would fall back into merely an oversight role, monitoring 'AI-to-AI interactions,'" ProPublica reported.
Google silent on AI drafting safety rules
Google did not respond to Ars' request to comment on this use case for Gemini, which could spread across government under Trump's direction.
Instead, the tech giant posted a blog on Monday, pitching Gemini for government more broadly, promising federal workers that AI would help with "creative problem-solving to the most critical aspects of their work."
Google has been competing with AI rivals for government contracts, undercutting OpenAI and Anthropic's $1 deals by offering a year of access to Gemini for $0.47.
The DOT contract seems important to Google. In a December blog, the company celebrated that DOT was "the first cabinet-level agency to fully transition its workforce away from legacy providers to Google Workspace with Gemini."
At that time, Google suggested this move would help DOT "ensure the United States has the safest, most efficient, and modern transportation system in the world."
Immediately, Google encouraged other federal leaders to launch their own efforts using Gemini.
"We are committed to supporting the DOT’s digital transformation and stand ready to help other federal leaders across the government adopt this blueprint for their own mission successes," Google's blog said.
DOT did not immediately respond to Ars' request for comment.

In early 2025, Forbes reports, investigators at the FBI served Microsoft with a warrant seeking the BitLocker encryption recovery keys for several laptops it believed held evidence of fraud in Guam's COVID-19 unemployment assistance program. And Microsoft complied with the FBI's request.
BitLocker is the name of the full-disk encryption technology that has been part of Windows for nearly two decades. Though initially only available to owners of the Pro editions of Windows who turned it on manually, during the Windows 8 era Microsoft began using BitLocker to encrypt local disks automatically for all Windows 11 Home and Pro PCs that signed in with a Microsoft account. Using BitLocker in this way also uploads a recovery key for your device to Microsoft's servers—this makes it possible to unlock your disk so you don't lose data if something goes wrong with your system, or if you install a CPU upgrade or some other hardware change that breaks BitLocker. But it also (apparently) makes it possible for Microsoft to unlock your disk, too.
A Microsoft rep said that the company handled "around 20" similar BitLocker recovery key requests from government authorities per year, and that these requests often fail because users haven't stored their recovery keys on Microsoft's servers. Microsoft and other tech companies have generally refused requests to install universal encryption backdoors for law enforcement purposes, and some companies (like Apple) claim to store device encryption keys using another layer of encryption that renders the keys inaccessible to the company.
But storing your device's recovery keys in someone else's cloud can still represent a privacy and security risk, especially at a time when the US government has become more interested in targeting journalists and the Trump administration's political opponents.
If you want to encrypt your Windows PC's disk but you don't want to store your recovery key with Microsoft, you do have options. We'll recap the requirements, as well as the steps you'll need to take.
You'll need Windows 11 Pro for this
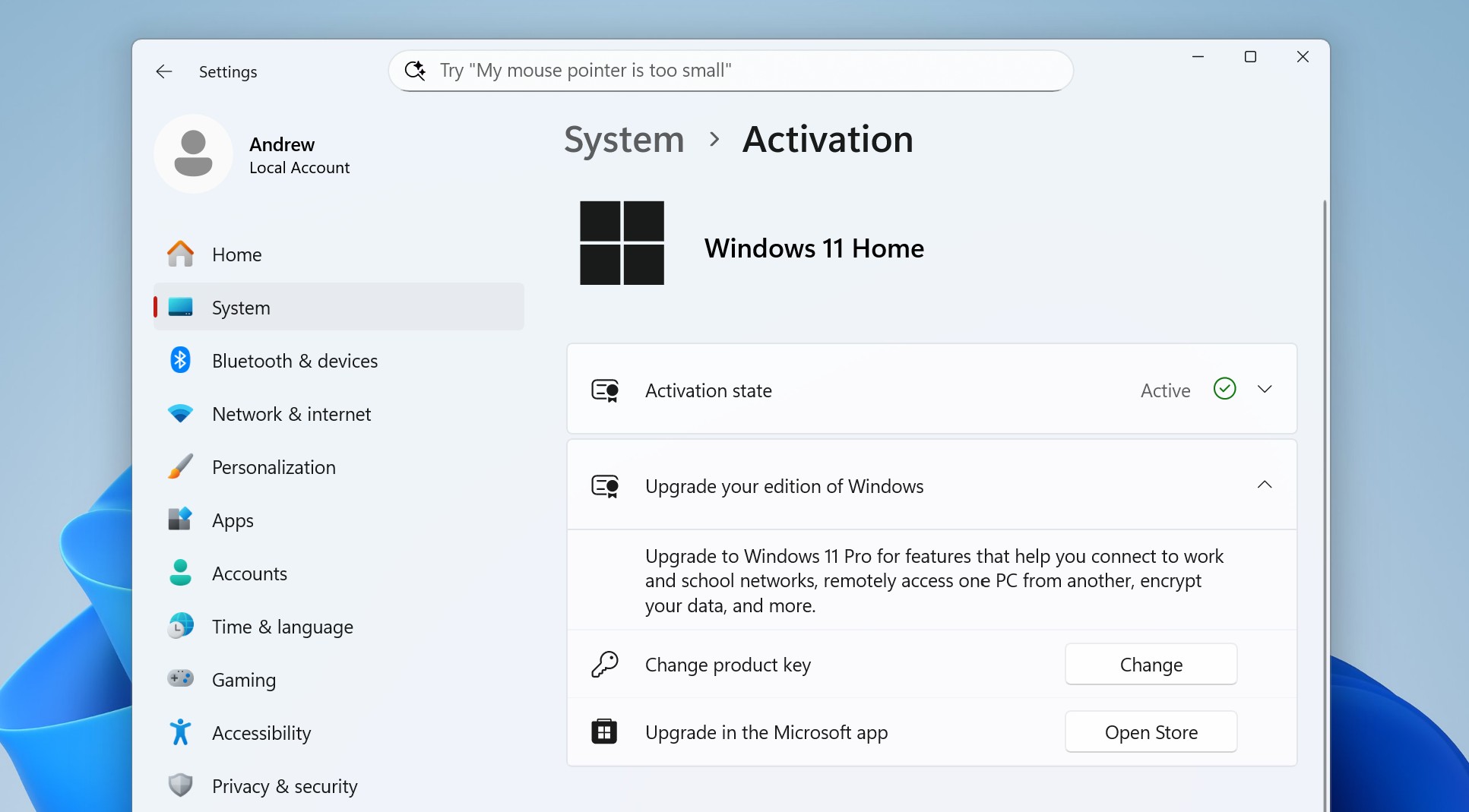 Settings > System > Activation will tell you what edition of Windows 11 you have and offer some options for upgrades.
Credit:
Andrew Cunningham
Settings > System > Activation will tell you what edition of Windows 11 you have and offer some options for upgrades.
Credit:
Andrew Cunningham
Before we begin: Disk encryption is one of the handful of differences between the Home and Pro versions of Windows.
Both the Home and Pro versions of Windows support disk encryption, but only the Pro versions give users full control over the process. The Home version of Windows only supports disk encryption when logged in with a Microsoft account and will only offer to store your encryption key on Microsoft's servers.
To access the full version of BitLocker and back up your own recovery key, you'll need to upgrade to the Pro version of Windows. Microsoft offers its own first-party upgrade option through the Microsoft Store for a one-time fee of $99, but it's also possible to bring your own product key and upgrade yourself. This Macworld-affiliated listing from StackCommerce claims to be an official Microsoft partner and is offering a Windows 11 Pro key for just $10, though your mileage with third-party key resellers may vary.
However you get it, once you have a valid key, open Settings, then System, then Activation, click upgrade your edition of Windows, click change product key, and then enter your Windows 11 Pro key (Windows 10 Pro keys should also work, if you already have one). Luckily, changing Windows editions doesn't require anything more disruptive than a system restart. You won't need to reinstall Windows, and you shouldn't lose any of your installed apps or data.
And once you've upgraded a PC to Windows 11 Pro once, you should be able to reinstall and activate Windows 11 Pro on that system again any time you want without having to re-enter your product key. Keep the product key stored somewhere, though, just in case you do need to use it for a reinstall, or if you ever need to re-activate Windows after a hardware upgrade.
Encrypting (or re-encrypting) your PC
Once you've got Windows 11 Pro set up, it's time to either encrypt or re-encrypt your disk.
If you've signed in with a Microsoft account, your disk is likely already encrypted, and the key is likely already stored on Microsoft's servers. If this is the case, this process will actually involve fully unencrypting and re-encrypting your drive, which can take an hour or two depending on the speed of your PC and the size of your drive.
Here's how to check your current encryption status and the steps to follow if you've already got a key backed up with Microsoft:
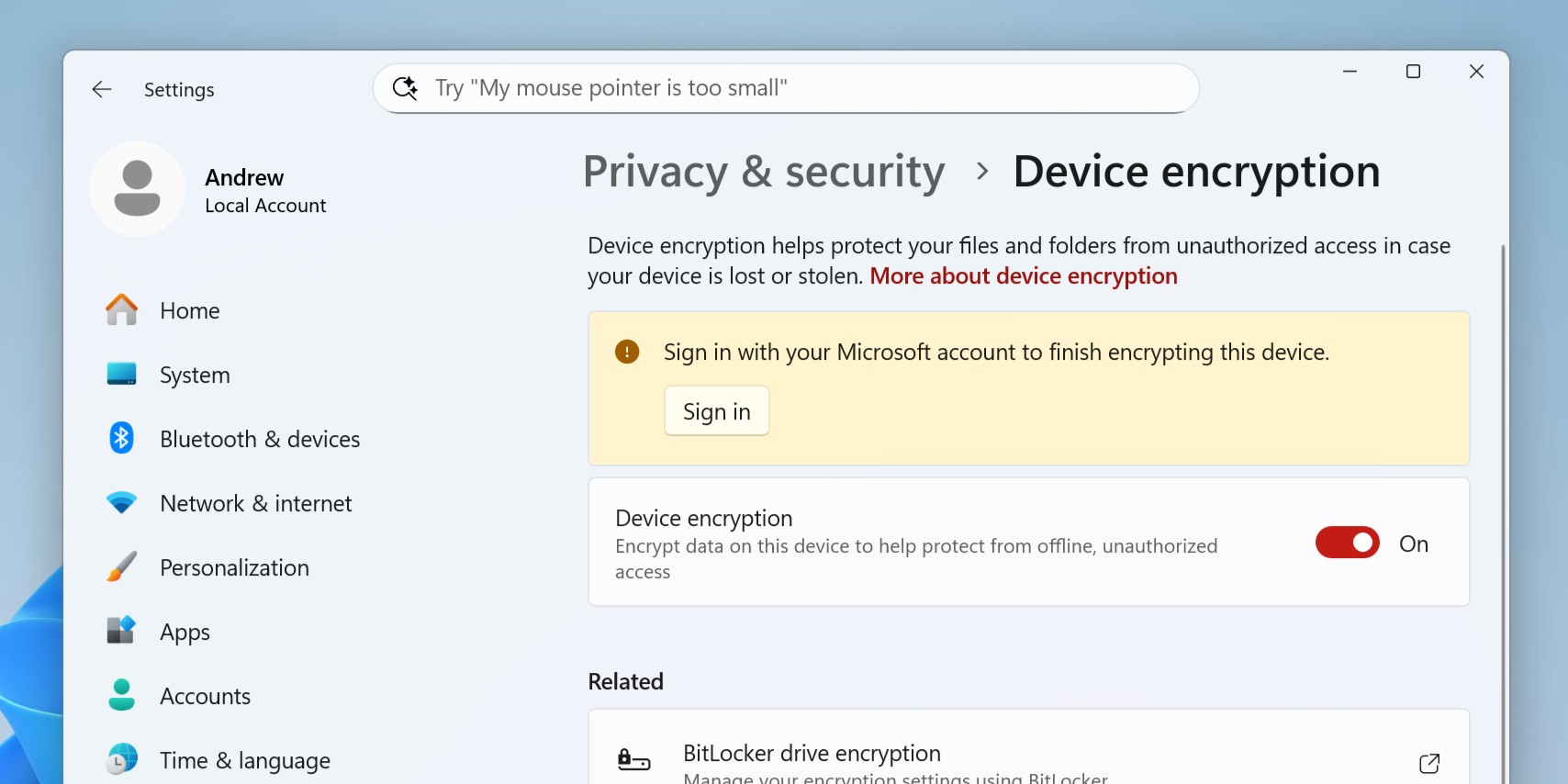 If you haven't signed in with a Microsoft account, you won't have a key saved to Microsoft's servers, and you can skip the decryption step.
Credit:
Andrew Cunningham
If you haven't signed in with a Microsoft account, you won't have a key saved to Microsoft's servers, and you can skip the decryption step.
Credit:
Andrew Cunningham
- Open the Settings app, click Privacy & security, and click Device encryption.
- If you see a notification about how you need to sign in with a Microsoft account to "finish encrypting this device," then you haven't saved your recovery key with Microsoft yet, and you can skip ahead to step 4.
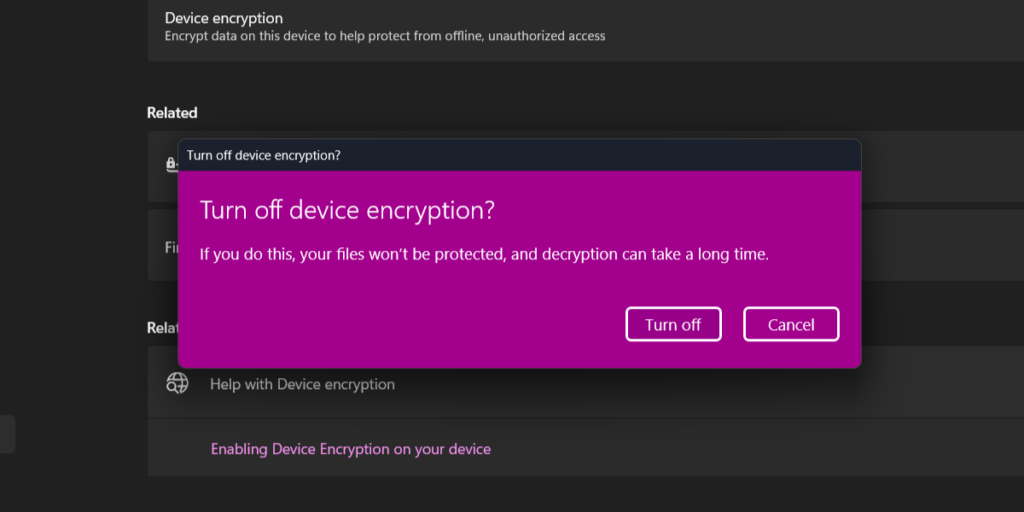
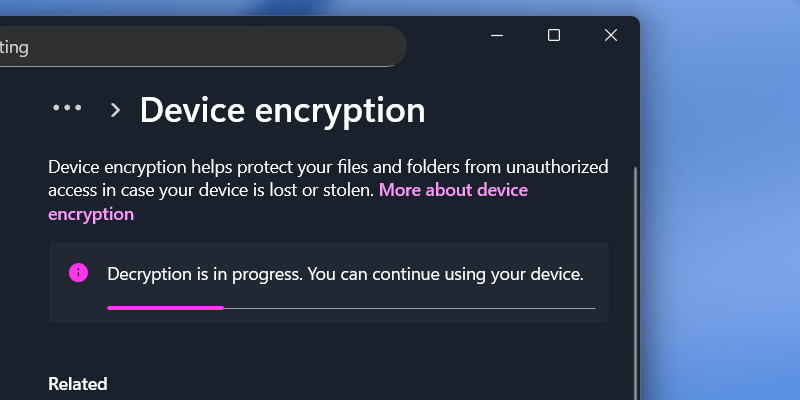
- If your device is already encrypted, the first thing you need to do is toggle that device encryption switch to off. You'll need to click through a confirmation screen and then wait for your disk to be decrypted. As Windows says, this may take a while.
- Once the disk is decrypted, click the BitLocker drive encryption button under the related subheading. It's a mark of how rarely Microsoft expects this setting to be used that this still opens up a legacy Windows Vista-era Control Panel, rather than opening up another section of the Settings app.
- Click the Turn on BitLocker link next to the C: drive and any other internal disk you want to encrypt. Now, you'll finally be able to do what we came here for: save a recovery key to a place other than a Microsoft account.
- You can print a physical copy of your recovery key and put it somewhere safe, or save the recovery key in a text file. If you choose this option, you'll need to be able to save the file to an external disk or a network drive—for obvious reasons, Windows won't let you save the recovery key to the disk you're about to encrypt, lest you end up with a drive you can't unlock.
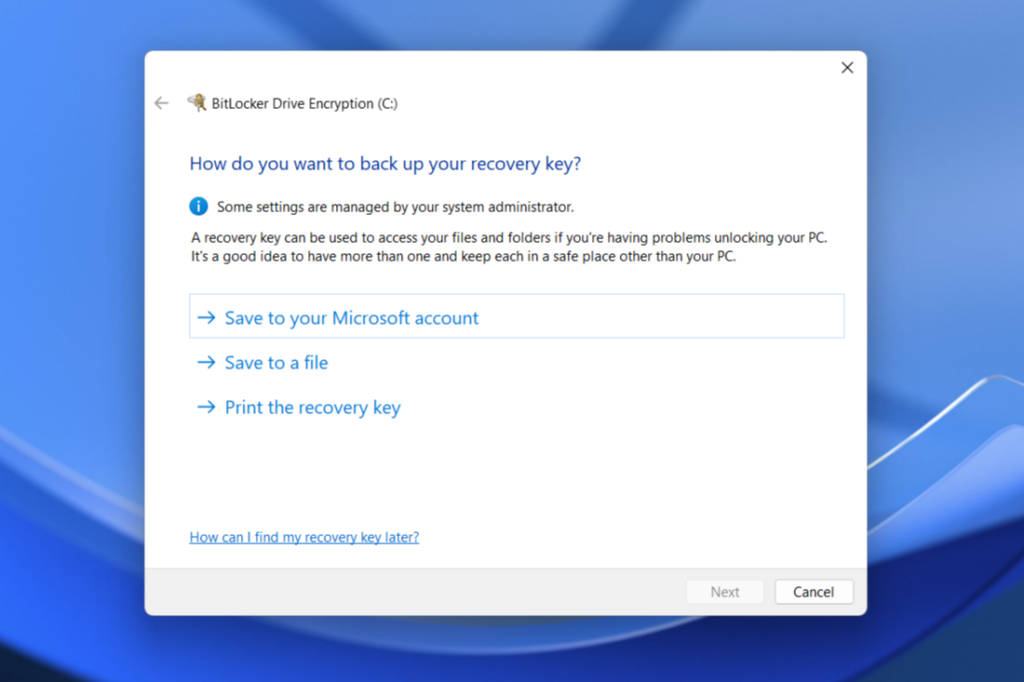
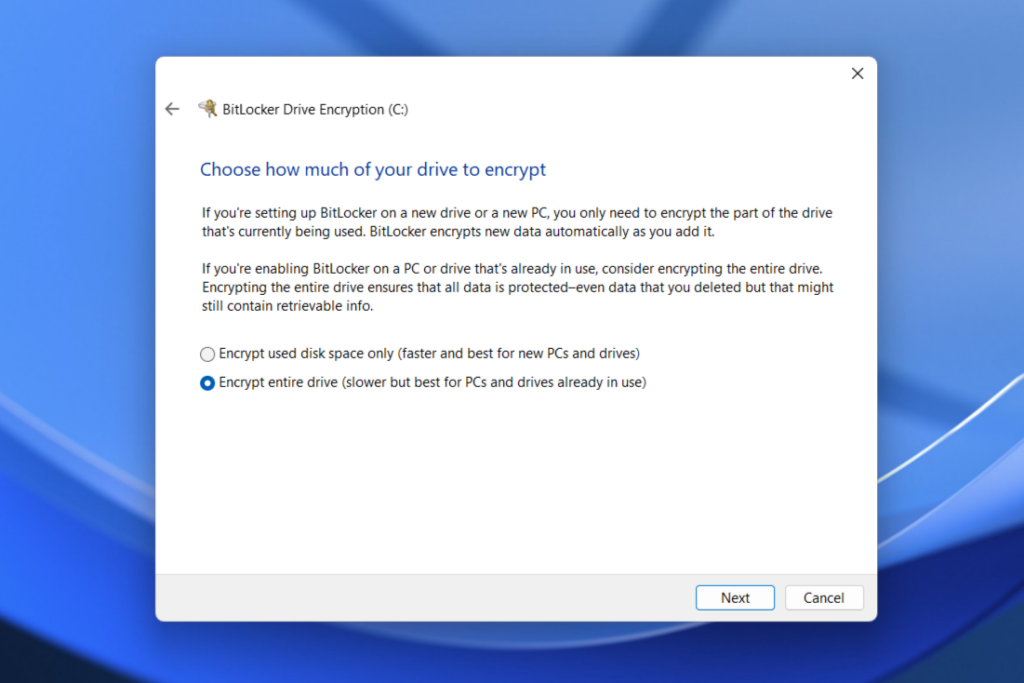
- With your recovery key saved, you'll be asked whether you'll just want to encrypt the portion of the disk you're using or the entire disk. I tend to prefer and recommend full-disk encryption, just to account for the possibility that previously deleted data might otherwise be recoverable from unencrypted parts of the drive, but the choice is up to you.
- You should also choose the "new encryption mode" when given the option, and I usually allow the system to run the BitLocker system check even though it's probably redundant for most PCs.
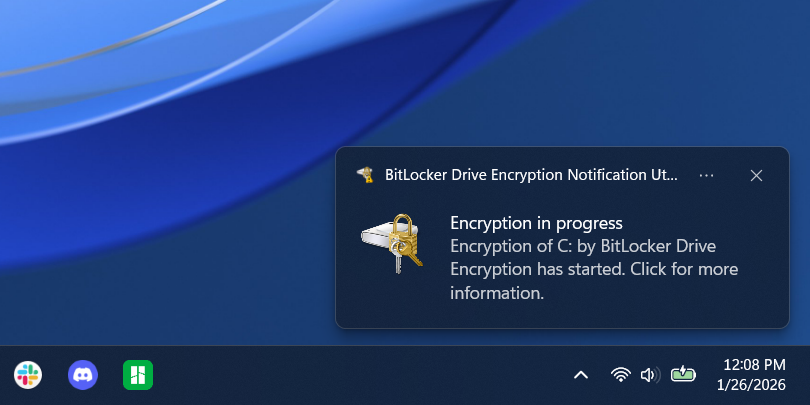
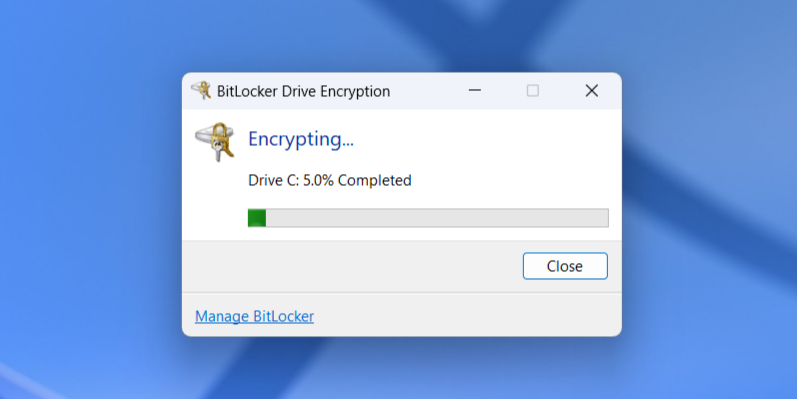
- After a restart, the encryption process will begin. Your drive will take some time to re-encrypt, based on the age of your PC and the settings you chose; progress can be tracked via an icon in the system tray.
Once your disk is re-encrypted, your PC should work just as it did before. The actual encryption technology hasn't changed at all—all we've done is change where the recovery key is saved.
This does put the burden on the user if and when it comes time to use your recovery key. You'll have to remember where you put it and not get it mixed up with any other recovery keys you've stored for other PCs or old Windows installations. But for anyone concerned about Microsoft giving their device's encryption keys to the government or anyone else with a valid subpoena, the extra hassle may be worth it in exchange for the added privacy and peace of mind.

